Which of the Following Triggers the Extrinsic Pathway of Coagulation
This is triggered by internal damage to the vessel wall By Joe D CC 30 via Wikimedia Commons. After adhesion degranulation from both types of granules takes place with the release of various factors.

Coagulation And Fibrinolysis Pathway Medical Make It Simple Cross Link
Factor III Tissue Factor or TF A condition in which platelet counts are low is known as _____.

. This pathway is quicker than the intrinsic pathway. The extrinsic pathway gets turned off after that and the intrinsic pathway takes over but at that point it doesnt matter. Clotting factor I is also known as fibrinogen.
The extrinsic and intrinsic coagulation pathways both lead into the final common pathway by independently activating factor X. This system is activated by vascular tissue trauma or surrounding extra-vascular tissue trauma. The extrinsic pathway involves initiation by factor III ie tissue factor and its interaction with factor VII.
The pathway of blood coagulation activated by tissue factor a protein extrinsic to blood is known as the extrinsic pathway Figure 1. What is intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Release of heparin from the liver.
Bottom line The INR activates the extrinsic pathway because in this test you add thromboplastin which contains both a tissue-factor-like substance and phospholipids to the test tube. Extrinsic Pathway The extrinsic pathway is activated by external trauma that causes blood to escape from the vascular system. Apoptosis the programmed death of a cell.
The extrinsic pathway. These external factors release a complex of several factors which is collectively known as tissue factor or tissue thromboplastin or factor III. The extrinsic pathway of coagulation is initiated by the.
The clotting cascade occurs through two separate pathways that interact the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathway. Release of tissue factor Factor III by damaged endothelium. The extrinsic pathway of coagulation is initiated by the sticking of platelets to damaged tissue.
Alternatively factor VII can. The following are the clotting factors involved in the process of blood clot formation. Tissue factor serves as a cofactor with factor VII to facilitate the activation of factor X.
The extrinsic pathway consists of factors I II VII and X. What is Extrinsic Pathway in Blood Clotting. Placing blood in a test tube initiates which pathway in the clotting process.
Primary hemostasis and secondary hemostasis. This is triggered by external trauma which causes blood to escape the circulation The intrinsic pathway. Activation of Factor VII exposed to collagen.
The intrinsic pathway is activated through exposed endothelial collagen and the extrinsic pathway is activated through tissue factor released by endothelial cells after external damage. Whereas factors XII XI IX and VIII are utilized in the intrinsic pathway. The following are serine proteases.
People with a normal coagulation system have a normal PT despite the fact that the extrinsic pathway only plays an initial role in coagulation. The pathway of blood coagulation activated by tissue factor a protein extrinsic to blood is known as the extrinsic pathway Figure 1. The intrinsic pathway consists of factors I II IX X XI and XII.
The PTT activates the intrinsic pathway because in this test. Factor VII is called stable factor. The bodily processes that prevent bleeding can be categorized into two mechanisms.
It involves factor VII. These are not serine proteases. Fibrinogen Concentration Fibrinogen or Factor I originates in the liver and is converted to fibrin by the enzyme thrombin during coagulation.
The final step in both pathways would be. It is synthesized by the liver. Which of the following affect almost every aspect of the clotting process.
Release of calcium occurs here. Where do clotting factors originate. Tissue factor is found in many of the cells of the body but is particularly abundant in those of the brain lungs and placenta.
Factors II VII IX X XI and XII. What triggers the Extrinsic Pathway of the coagulation phase. Calcium binds to the phospholipids that appear secondary to the platelet activation and provides a surface for assembly of various coagulation factors.
Vasoconstriction and the formation of platelet plug are the two processes of primary. Main Difference Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Pathways in Blood Clotting. Damages trauma to blood vessels cause bleeding.
Alternatively factor VII can activate factor IX which in turn can activate. The extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation is also known as the tissue factor pathway and refers to a cascade of enzymatic reactions resulting in blood clotting. In contrast the intrinsic pathway is initiated through the release of signal factors by mitochondria within the cell.
Tissue factor serves as a cofactor with factor VII to facilitate the activation of factor X. Fibrinogen is the last enzyme to be activated in the process of clot formation. Extrinsic pathway is another way of blood coagulation.
The extrinsic pathway is initiated through the stimulation of the transmembrane death receptors such as the Fas receptors located on the cell membrane. The extrinsic pathway requires something extrinsic to the blood tissue factor for it to run. A registered nurse is teaching a student nurse about the features of the extrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade.
Also to know is which of the following triggers the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Blood coagulation is initiated by either the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway. Fibrin has been formed and the test is done.
It is downstream of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Factors V VIII XIII. Respectively each one is named fibrinogen prothrombin Christmas factor Stuart-Prower factor plasma thromboplastin and Hageman factor.
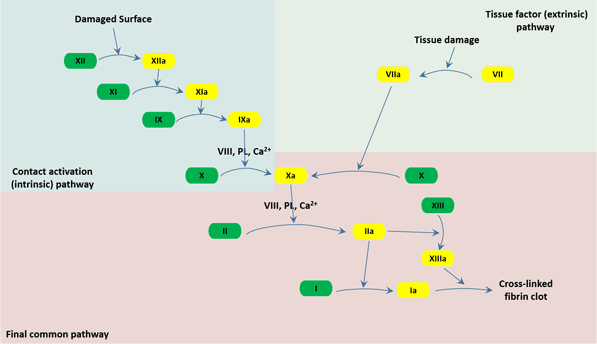
The Overview Of Coagulation Cusabio

Hemostasis Anatomy And Physiology Ii
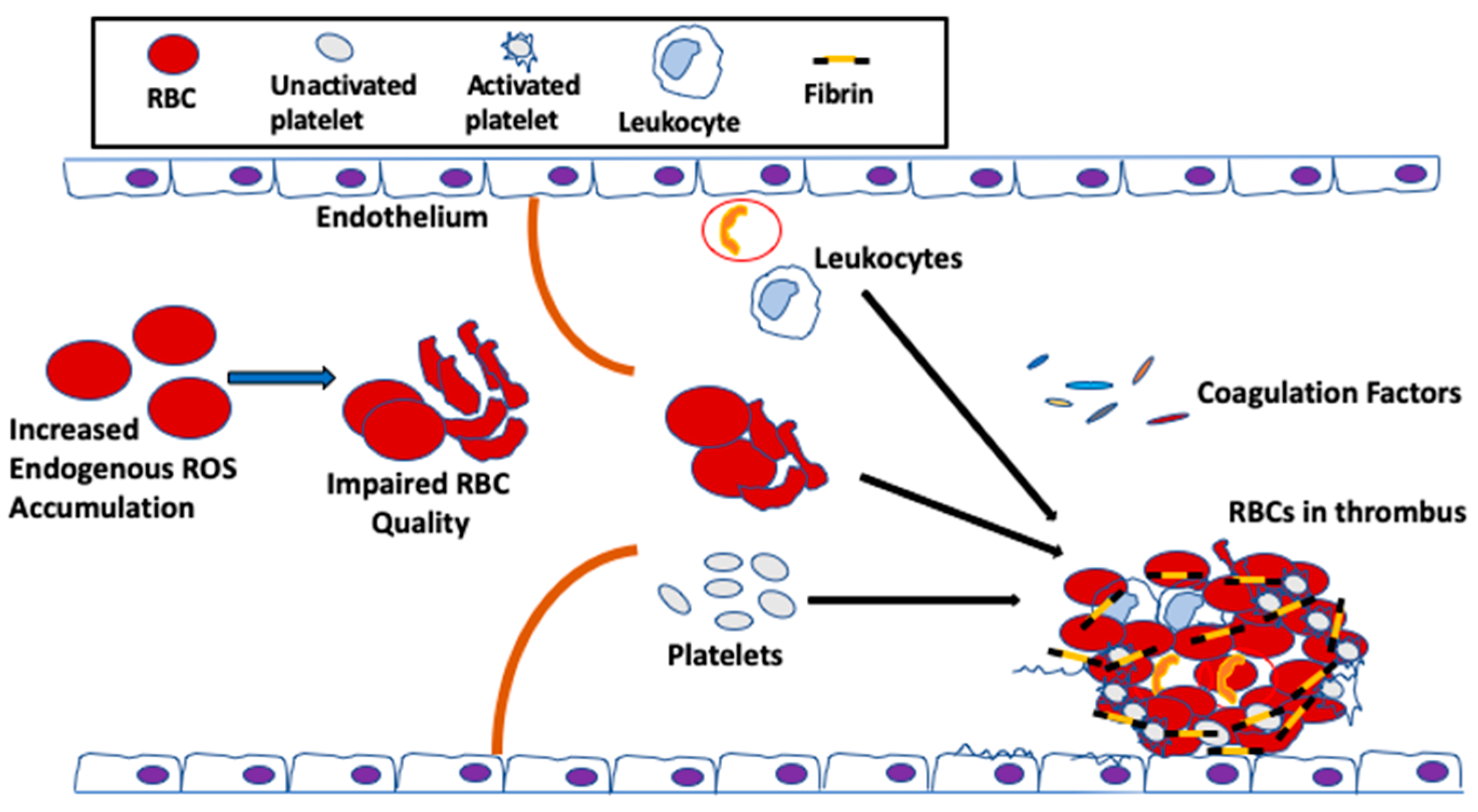
Ijms Free Full Text Oxidative Stress And Thrombosis During Aging The Roles Of Oxidative Stress In Rbcs In Venous Thrombosis Html

The Intrinsic Extrinsic And Common Pathways Of The Coagulation Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Representation Of The Coagulation Cascade And The Download Scientific Diagram

Difference Between Intrinsic And Extrinsic Pathways In Blood Clotting Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Bleeding And Blood Clotting Intrinsic Pathway Of Blood Coagulation Britannica

Coagulation Cascade What Is It Steps And More Osmosis
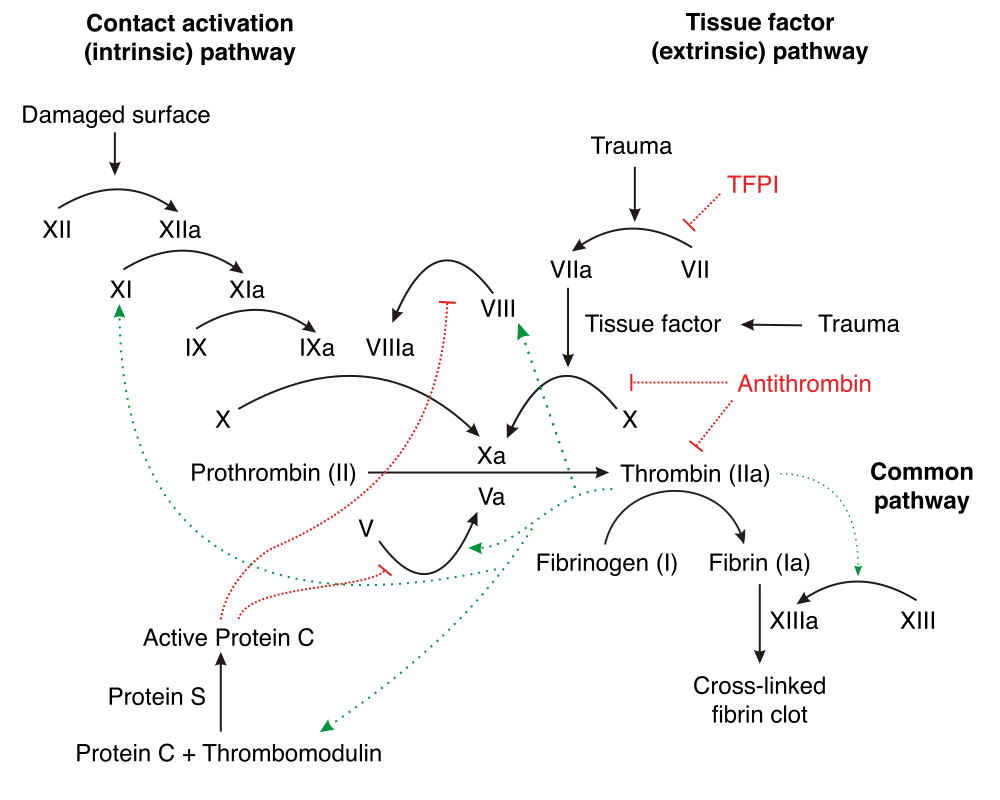
Coagulation Intrinsic Extrinsic Fibrinolysis Teachmephysiology

Schematic Diagram Of The Different Pathways Of Blood Coagulation In Download Scientific Diagram

Coagulation Cascade Poster Medical Technology Coagulation Cascade Medical Lab Technician

Overview Of Hemostasis There Are Two Pathways To Initiate Coagulation Download Scientific Diagram

The Intrinsic Extrinsic And Common Pathways Of The Coagulation Download Scientific Diagram

Initiation Phase Of Hemostasis The Intrinsic Pathway Within The Download Scientific Diagram
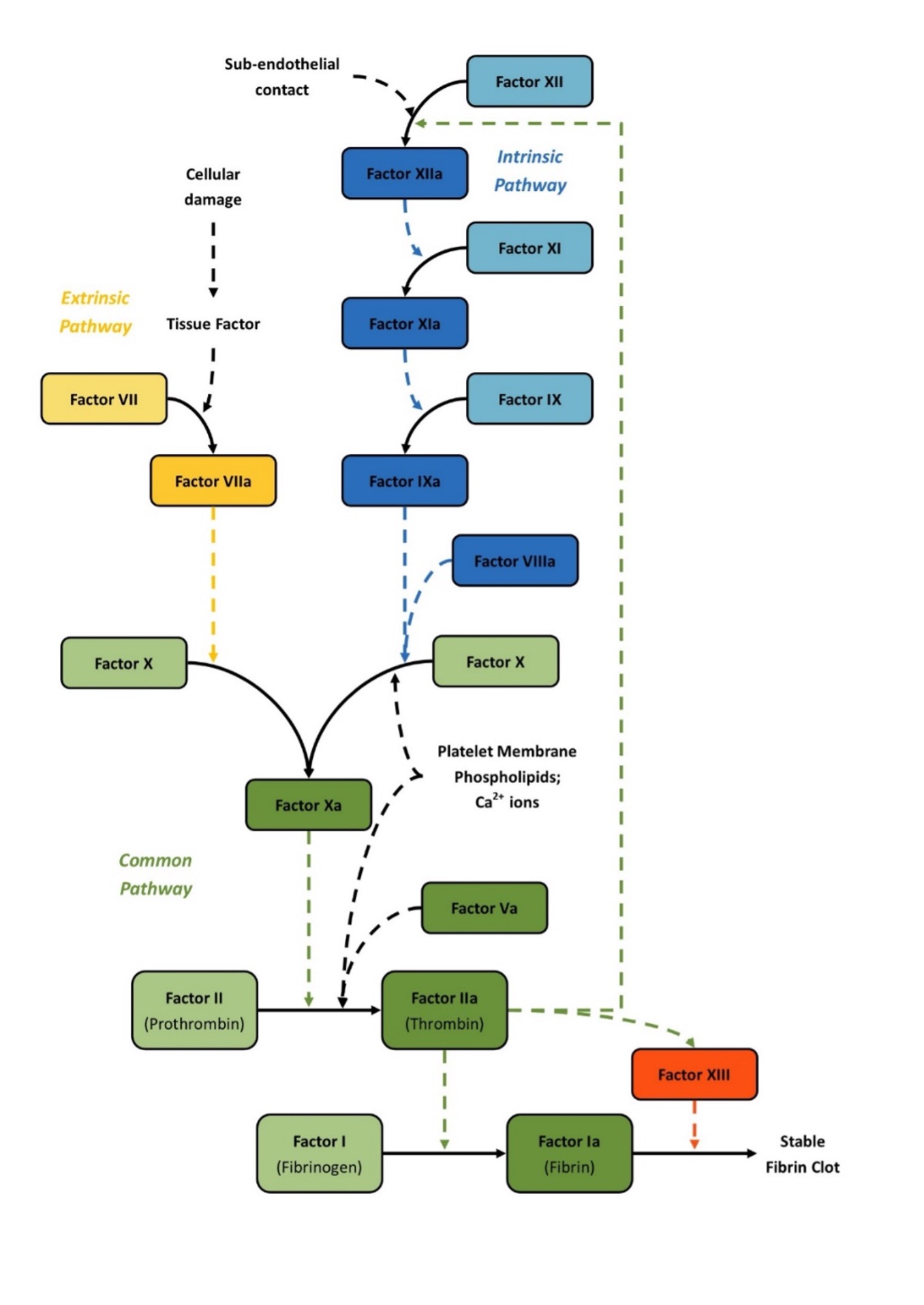
Coagulation Cascade Intrinsic Extrinsic Geeky Medics
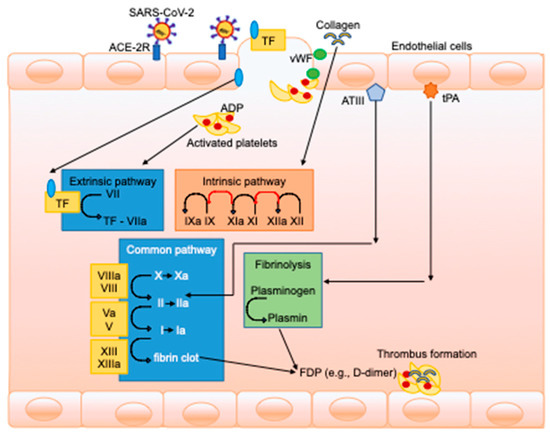
Jcm Free Full Text Coagulative Disorders In Critically Ill Covid 19 Patients With Acute Distress Respiratory Syndrome A Critical Review Html

Bleeding And Blood Clotting Intrinsic Pathway Of Blood Coagulation Britannica

Comments
Post a Comment